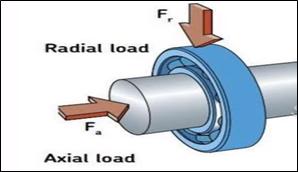
Piyali Group Corporation is the proud designer and manufacturer of best-in-class 200 TPD thrust roller assembly parts. Our products perform a variety of functions in many factories and industries. An axial load bearing used to handle axial loads, which act parallel to the axis of rotation. A thrust roller typically consists of two thrust washers or races, a shaft, and a cylindrical roller. These cylindrical rollers are perpendicular to the axis of rotation and typically reside in a frame.
The 200 TPD thrust roller assembly typically consists of various parts such as:
- Thrust roller
- Thrust roller shaft plate
- Thrust support system
- Thrust roller bearings
- Thrust roller sleeves
- Thrust roller base plate
THRUST ROLLER ASSEMBLY PARTS:
- Thrust Roller: The thrust roller supports the kiln’s weight and enables smooth rotation. It is typically a large cylindrical piece of steel or cast iron that can endure heavy weights and high temperatures.
- Thrust roller shaft plate: A thrust roller shaft plate is a part of a rotary kiln that supports the weight of the machine and facilitates smooth rotation. The thrust roller shaft plate attaches to the kiln shell and normally uses heavy steel material.
- Thrust Support System: The thrust support system transmits the load from the thrust roller to the support structure. In order to ensure the thrust roller operates smoothly and effectively, this system also contains a lubricating system.
- Thrust Roller Bearings: Thrust roller bearings are a particular type of rolling-element bearing that is capable of supporting axial loads, or loads that work perpendicular to the axis of rotation.
- Thrust roller sleeves are parts of rotary kilns that help the machine rotate smoothly and sustain the weight of the apparatus.
- The thrust roller plate serves to uniformly transfer the load from the rotary kiln across the roller. Thrust roller plates usually consist of cast iron or flat steel.
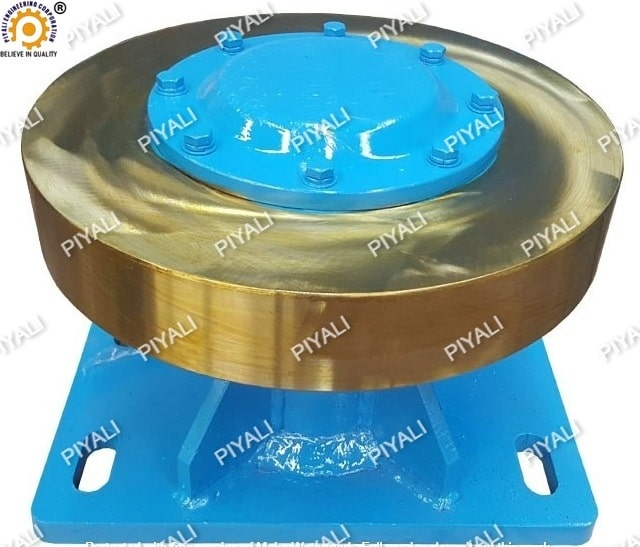

WORKING PROCESS: THRUST ROLLER ASSEMBLY
A thrust roller assembly transfers thrust or axial loads between two rotating machine components, distributing them equally across the rollers. When a thrust force applies, the rollers rotate and roll, distributing the load evenly. The cage and eventually the other machine part receive the force after it has been transferred from the rollers to the cage. The direction of the thrust load determines the type of thrust roller assembly.
The direction of the thrust load determines the type of thrust roller assembly required. As an illustration, a thrust load in the axial direction requires a roller bearing or thrust ball , while a radial thrust load requires a cylindrical roller bearing.
KEY FEATURES OF THRUST ROLLER ASSEMBLY:
- Thrust roller assemblies endure high axial loads and support heavy rotating machinery.
- Thrust rollers create minimal friction, resulting in efficient transmission of forces and minimal wear.
- Rollers in thrust roller assemblies are designed to withstand high speeds without damage.
- For thrust roller assemblies, materials selection is based on operating conditions, corrosion resistance, and strength.
- Thrust roller assemblies reduce stress and wear.
- Thrust roller assemblies are available in a variety of designs, such as tapered roller bearings, cylindrical roller bearings, and thrust ball bearings, which makes them ideal for a variety of uses.
1. THRUST ROLLER:
A thrust roller is one that holds weights parallel to its axis of rotation or is capable of bearing axial loads. Thrust rollers are found in many industrial settings where it is necessary to support and handle axial loads, such as in rotary kilns and other large machinery. Machinery needs to be correctly designed and maintained in order to operate efficiently and securely. They are able to handle heavy loads and difficult working conditions.
A thrust roller typically consists of two thrust washers or races, a shaft, and a cylindrical roller. The thrust washers or races are able to bear against the ends of the roller in order to prevent axial movement, while the cylindrical roller helps to take axial stresses and revolves on the shaft.

2. THRUST ROLLER SHAFT PLATE:
Thrust roller shaft plate: A thrust roller shaft plate is a part of a rotary kiln that supports the weight of the machine and facilitates smooth rotation. The thrust roller shaft plate serves to uniformly transfer the load from the rotary kiln across the roller. Thrust roller plates usually consist of cast iron or flat steel.
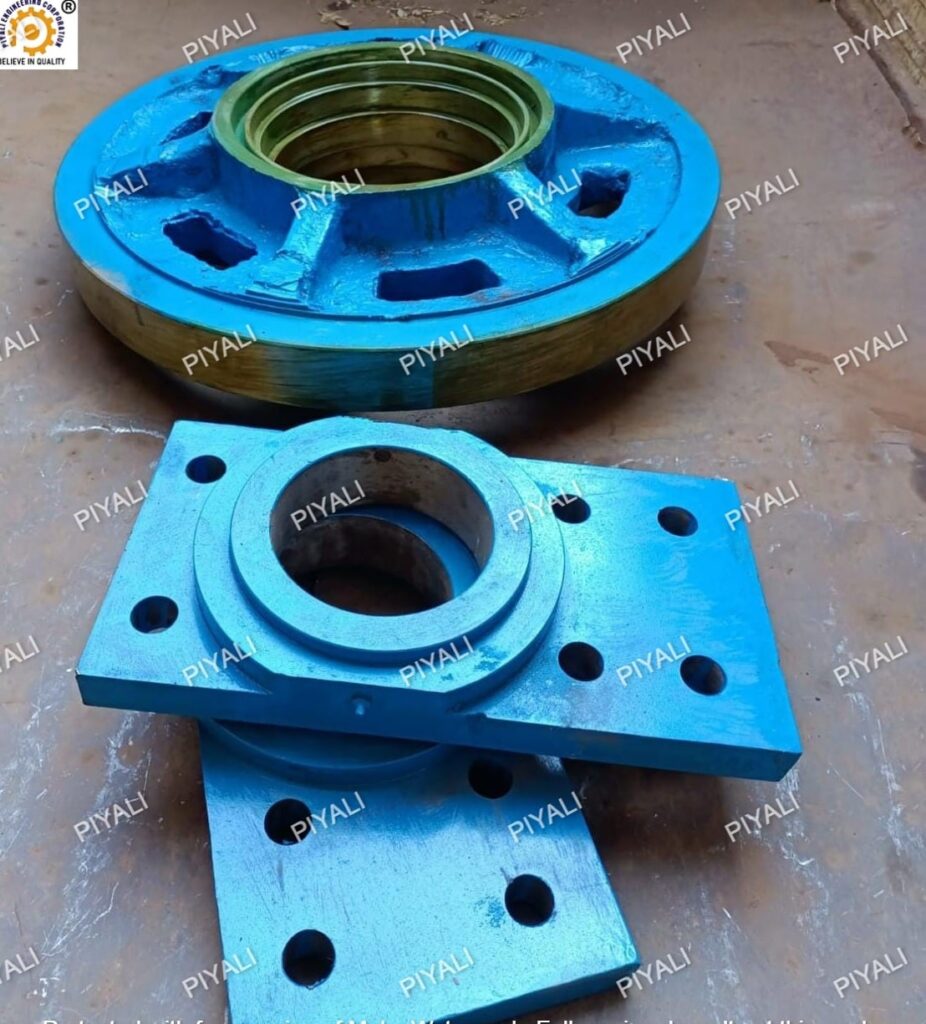

Function of Thrust roller shaft plate:
The thrust roller shaft plate’s function is to transfer the weight of the kiln to the support rollers, who then move it to the supporting framework. The plate bears the equipment’s tremendous weight uniformly over the support rollers.
The thrust roller shaft plate typically stays in place with a number of bolts that are tightened to a specific force. If these bolts are overtightened, the plate or the support rollers get damaged, and if they are undertightened, the components may fail or wear out more quickly. It is essential to guarantee that these fasteners are set properly.
How it works:
The rotating kiln’s shell attaches to the thrust roller shaft plate. Frequently, several bolts that are tightened to a specific torque serve to secure it in position. The thrust roller shaft plate receives the weight of the rotating kiln and transfers it to the support rollers in an even distribution. The rotary kiln rotates smoothly because the support rollers revolve on separate shafts. The thrust roller shaft plate originates in order to endure the significant weight put on the equipment and safely transmit the kiln’s force to the support rollers.
3. THRUST SUPPORT SYSTEM:
The thrust support system consists of support bearings and other components that assist in transferring the weight from the thrust roller to the support structure. In order to ensure the thrust roller operates smoothly and effectively, this system also contains a lubricating system.
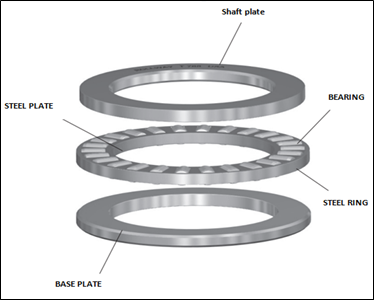
4.THRUST ROLLER BEARINGS:
Thrust roller bearings are a particular type of rolling-element bearing that supports axial loads, or loads that work perpendicular to the axis of rotation. The thrust raceway and the rollers are the two primary parts of these bearings. The smooth or slightly curved thrust raceway’s purpose is to maintain the axial pressure. It is a vital component of the bearing assembly and typically goes on a shaft or housing.
As they travel along the thrust raceway, they serve to transfer the axial load from one component to another. Usually, a number of metal sleeves divide the rollers from one another, helping to maintain the rollers’ precise alignment inside the bearing.
Depending on the quantity of thrust raceways and rollers, thrust roller bearings can be either single direction or double direction. Single-direction bearings are able to handle axial loads in one direction, whereas double-direction bearings are capable of handling them in both directions.They work particularly effectively in situations that require accurate axial alignment and large axial loads, as well as high speeds. Thrust roller bearings are a significant type of bearing that are essential in many mechanical systems, helping to transmit axial loads and assuring dependable and smooth functioning.
5. THRUST ROLLER SLEEVES:
Thrust roller sleeves help the machine rotate smoothly and sustain the weight of the apparatus. The high-strength steel sleeves have a cylindrical shape and can withstand heavy loads. The thrust roller sleeves work to fasten the support rollers, which rotate on their own axles and support the weight of the kiln.The sleeves distribute the load equally across the support rollers and give the kiln a smooth surface on which to rotate. Consequently, a thrust roller bearings sleeves are vital to the performance and longevity of the bearing by ensuring the bearing’s proper alignment and operation.

To guarantee the safe and reliable operation of the rotary kiln, regular maintenance of the thrust roller sleeves are necessary. Replace the sleeves immediately in order to stop further damage and guarantee the equipment’s long-term functionality. Generally, sleeves help to separate the rollers and keep them in the appropriate alignment within the bearing. The steel ring or sleeve is positioned between the thrust raceway and the rollers. They work to reduce friction between the raceway and the rollers and to distribute the weight evenly over the rollers.
6. THRUST ROLLER BASE PLATE:
The thrust plate serves to uniformly transfer the load from the rotary kiln across the roller by sitting on top of the thrust roller and usually consist of cast iron or flat steel. Moreover, it offers a surface for the kiln to rotate on and aids in reducing the thrust roller’s wear and tear.
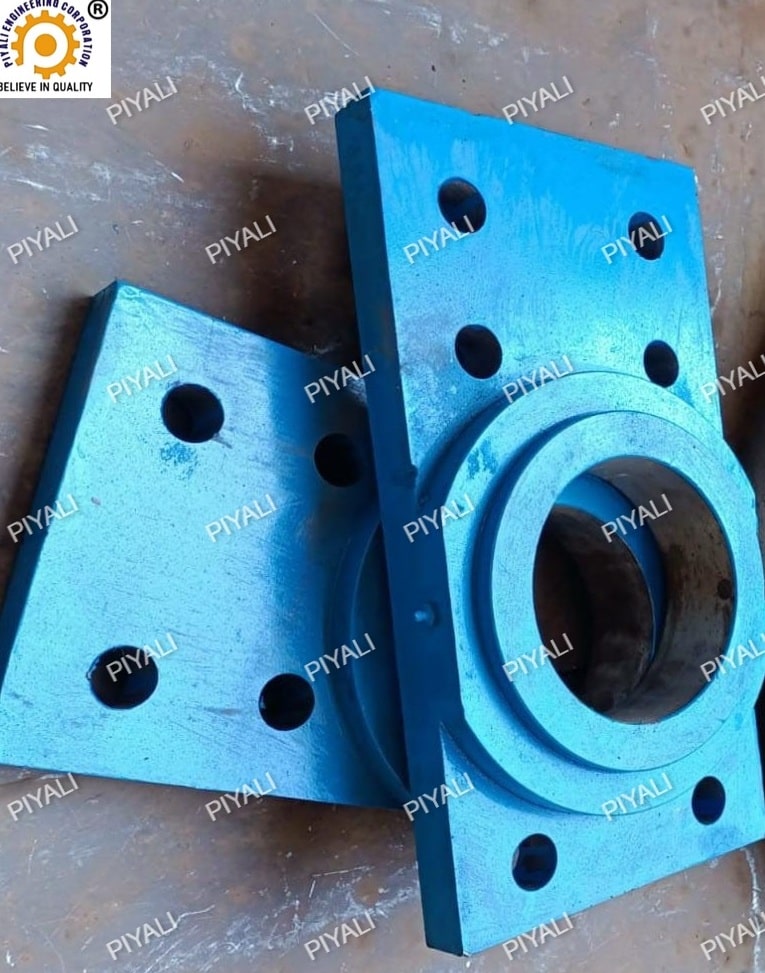

The thrust roller assembly used in rotary kilns includes the thrust roller base plate as one of its parts. It is a flat plate made of cast iron or steel that fits on top of the thrust roller and aids in uniformly dispersing the load from the rotary kiln across the roller. The base plate also serves as a surface for the kiln to rotate on and aids in limiting the thrust roller’s rate of wear.

